The computer vision system based on artificial intelligence (AI) technology can estimate various motion indices (GDI – Gait Deviation Index, Cadence – step rhythm, Speed – movement speed, Knee Flexion – thigh muscle flexibility index) from videos with an accuracy of approximately 80% compared to modern motion tracking camera systems (Motion Capture Systems or Mocap). This result opens up opportunities for developing cost-effective smart healthcare solutions for screening and evaluating motion abnormalities or assessing the recovery progress of patients on a large scale. The algorithm was developed by Le Thanh Quoc Hung, a third-year student at the College of Engineering and Computer Science, and a research assistant at the VinUni-Illinois Smart Health Center, VinUniversity. This research got accepted to the 21st IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, which will be held in Athens, Greece, May 27-30, 2024.
 Le Thanh Quoc Hung – A third-year student at the College of Engineering and Computer Science, and a research assistant at the VinUni-Illinois Smart Health Center, VinUniversity.
Le Thanh Quoc Hung – A third-year student at the College of Engineering and Computer Science, and a research assistant at the VinUni-Illinois Smart Health Center, VinUniversity.
Musculoskeletal diseases and cognitive impairments in patients lead to difficulties in movement as well as negative effects on their psychological health. Clinical gait analysis, a vital tool for early diagnosis and treatment, traditionally relies on expensive optical motion capture systems. Recent advances in computer vision and deep learning have opened the door to more accessible and cost-effective alternatives. This paper introduces a novel spatiotemporal Transformer network to estimate critical gait parameters from RGB videos captured by a single-view camera. Empirical evaluations on a public dataset of cerebral palsy patients indicate that the proposed framework surpasses current state-of-the-art approaches and shows significant improvements in predicting general gait parameters (including Walking Speed, Gait Deviation Index – GDI, and Knee Flexion Angle at Maximum Extension) while utilizing fewer parameters and alleviating the need for manual feature extraction. In the future, we will collaborate with the Vinmec 3D Motion Lab to test our motion analysis algorithms on real data and progress toward the development of new clinical applications.
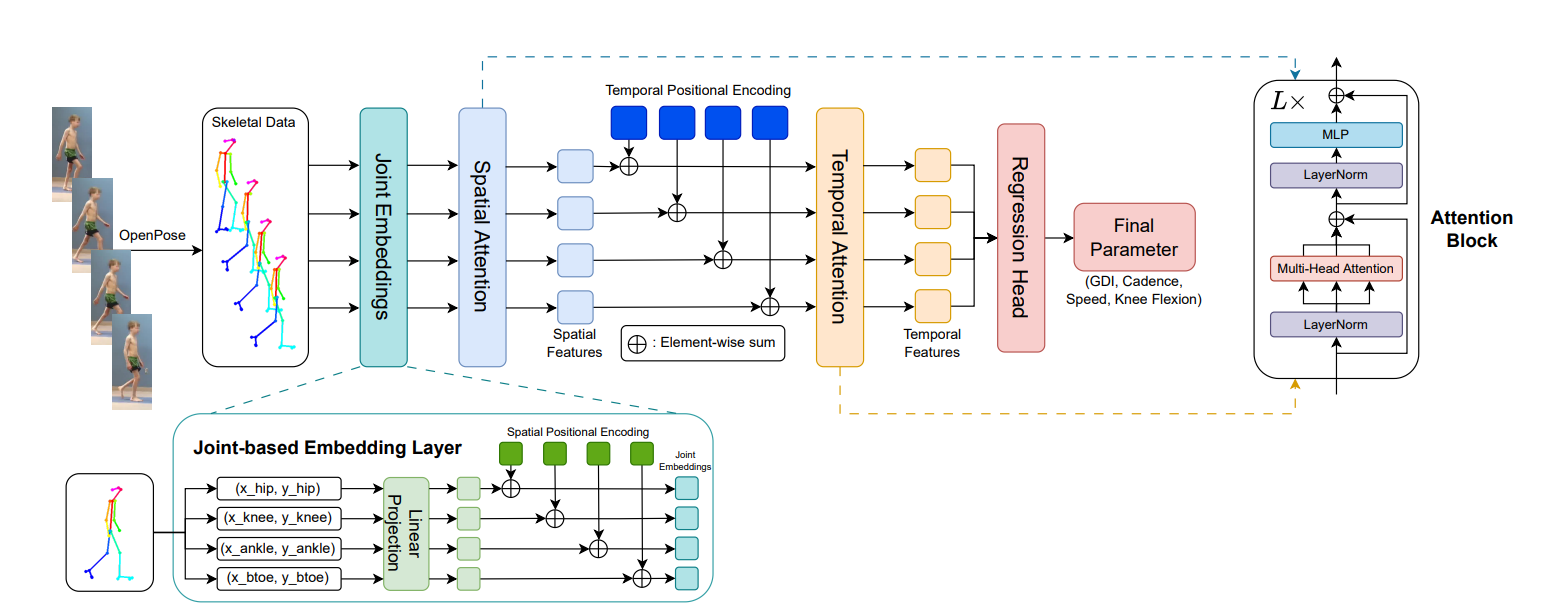 Overview of the computer vision system based on artificial intelligence (AI) technology that can estimate various motion indices. It first projects the 2D coordinates of each joint to a D-dimensional space. The architecture has two attention blocks: spatial and temporal attention blocks. The spatial attention block extracts spatial information by attending to every other joint in the same frame. The temporal attention block captures temporal dependencies among the frames given a motion sequence. Lastly, it use a Fully Connected Neural Network to output the final parameters..
Overview of the computer vision system based on artificial intelligence (AI) technology that can estimate various motion indices. It first projects the 2D coordinates of each joint to a D-dimensional space. The architecture has two attention blocks: spatial and temporal attention blocks. The spatial attention block extracts spatial information by attending to every other joint in the same frame. The temporal attention block captures temporal dependencies among the frames given a motion sequence. Lastly, it use a Fully Connected Neural Network to output the final parameters..
The ISBI conference series is jointly organized by the IEEE Signal Processing Society and the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, and its top priority is to strengthen the synergy between researchers and experts from academia, healthcare organizations, research institutions, and industry towards advancing research and innovation in the field of biomedical imaging. ISBI will cover all areas related to medical image computing, it will extend its focus to emerging AI frontiers in biomedical imaging, including interpretability, domain shifts and adaptation, trustworthiness, as well as on issues related to in-silico modelling, virtual twins, precision medicine, and clinical applications. The 2024 ISBI edition will be an in-person meeting that will take place at the Megaron Athens International Conference Center.
The full-text of the paper can be accessed here.
VISHC Team